Here are some events that happened on April 30th. It could be an event or a person that died or was born on that day
1770 Born: David Thompson, English-Canadian cartographer and explorer (d. 1857)
David Thompson (30 April 1770 – 10 February 1857) was a British-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and cartographer, known to some native peoples as Koo-Koo-Sint or "the Stargazer". Over Thompson's career, he traveled some 90,000 kilometers (56,000 mi) across North America, mapping 4.9 million square kilometers (1.9 million square miles) of North America along the way. For this historic feat, Thompson has been described as the "greatest practical land geographer that the world has produced".
Canadian stamp issued to commemorate David Thompson
1777 Born: Carl Friedrich Gauss, German mathematician and physicist (d. 1855)
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (Latin: Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 1777 – 23 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes referred to as the Princeps mathematicorum (Latin for '"the foremost of mathematicians"') and "the greatest mathematician since antiquity", Gauss had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science, and is ranked among history's most influential mathematicians.
German stamp and First Day Cover depicting Gauss
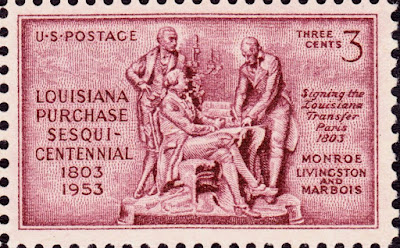
1803 – Louisiana Purchase: The United States purchases the Louisiana Territory from France for $15 million, more than doubling the size of the young nation.
The Louisiana Purchase (French: Vente de la Louisiane 'Sale of Louisiana') was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from France in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, the U.S. acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi (2,140,000 km2; 530,000,000 acres). The treaty was negotiated by French Treasury Minister François Barbé-Marbois (acting on behalf of Napoleon) and American delegates James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston (acting on behalf of President Thomas Jefferson).
The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1699 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, then the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana as part of a broader project to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to put down a revolt in Saint-Domingue, coupled with the prospect of renewed warfare with the United Kingdom, prompted Napoleon to consider selling Louisiana to the United States.
Here are some US stamps and a First Day Cover depicting the Louisiana Purchase
1812 – The Territory of Orleans becomes the 18th U.S. state under the name Louisiana.
Louisiana is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 19th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties. The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans.
Much of the state's lands were formed from sediment washed down the Mississippi River, leaving enormous deltas and vast areas of coastal marsh and swamp. These contain a rich southern biota; typical examples include birds such as ibises and egrets. There are also many species of tree frogs, and fish such as sturgeon and paddlefish. In more elevated areas, fire is a natural process in the landscape and has produced extensive areas of longleaf pine forest and wet savannas. These support an exceptionally large number of plant species, including many species of terrestrial orchids and carnivorous plants. Louisiana has more Native American tribes than any other southern state, including four that are federally recognized, ten that are state recognized, and four that have not received recognition.
Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th-century French, Haitian, Spanish, French Canadian, Native American, and African cultures that they are considered to be exceptional in the U.S. Before the American purchase of the territory in 1803, the present-day State of Louisiana had been both a French colony and for a brief period a Spanish one. In addition, colonists imported numerous African people as slaves in the 18th century. Many came from peoples of the same region of West Africa, thus concentrating their culture. In the post-Civil War environment, Anglo-Americans increased the pressure for Anglicization, and in 1921, English was for a time made the sole language of instruction in Louisiana schools before a policy of multilingualism was revived in 1974. There has never been an official language in Louisiana, and the state constitution enumerates "the right of the people to preserve, foster, and promote their respective historic, linguistic, and cultural origins".
Based on national averages, Louisiana frequently ranks low among the U.S. in terms of health, education, and development, and high in measures of poverty. In 2018, Louisiana was ranked as the least healthy state in the country, with high levels of drug-related deaths and excessive alcohol consumption, while it has had the highest homicide rate in the United States since at least the 1990s.
US Louisiana Statehood stamps
1905 – Albert Einstein completes his doctoral thesis at the University of Zurich.
Albert Einstein (14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics). His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He is best known to the general public for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory.
The son of a salesman who later operated an electrochemical factory, Einstein was born in the German Empire but moved to Switzerland in 1895 and renounced his German citizenship in 1896. Specializing in physics and mathematics, he received his academic teaching diploma from the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School (German: eidgenössische polytechnische Schule) in Zürich in 1900. The following year, he acquired Swiss citizenship, which he kept for his entire life. After initially struggling to find work, from 1902 to 1909 he was employed as a patent examiner at the Swiss Patent Office in Bern.
Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led him to develop his special theory of relativity during his time at the Swiss Patent Office. In 1905, called his annus mirabilis (miracle year), he published four groundbreaking papers, which attracted the attention of the academic world; the first outlined the theory of the photoelectric effect, the second paper explained Brownian motion, the third paper introduced special relativity, and the fourth mass-energy equivalence. That year, at the age of 26, he was awarded a PhD by the University of Zurich.
Although initially treated with skepticism from many in the scientific community, Einstein's works gradually came to be recognised as significant advancements. He was invited to teach theoretical physics at the University of Bern in 1908 and the following year moved to the University of Zurich, then in 1911 to Charles University in Prague before returning to ETH (the newly renamed Federal Polytechnic School) in Zürich in 1912. In 1914, he was elected to the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, where he remained for 19 years. Soon after publishing his work on special relativity, Einstein began working to extend the theory to gravitational fields; he then published a paper on general relativity in 1916, introducing his theory of gravitation. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties of light and the quantum theory of radiation, the basis of the laser, which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, he applied the general theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe.
In 1933, while Einstein was visiting the United States, Adolf Hitler came to power. Because of his Jewish background, Einstein did not return to Germany. He settled in the United States and became an American citizen in 1940. On the eve of World War II, he endorsed a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt alerting FDR to the potential development of "extremely powerful bombs of a new type" and recommending that the US begin similar research. This eventually led to the Manhattan Project. Einstein supported the Allies, but he generally denounced the idea of using nuclear fission as a weapon. He signed the Russell–Einstein Manifesto with British philosopher Bertrand Russell, which highlighted the danger of nuclear weapons. He was affiliated with the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, until his death in 1955.
He published more than 300 scientific papers and more than 150 non-scientific works. His intellectual achievements and originality have made the word "Einstein" synonymous with "genius". Eugene Wigner compared him to his contemporaries, writing that "Einstein's understanding was deeper even than Jancsi von Neumann's. His mind was both more penetrating and more original".
Stamps from various countries depicting Albert Einstein