Here are some events that happened on August 8th. It could be an event or a person that died or was born on that day
1786 – Mont Blanc on the French-Italian border is climbed for the first time by Jacques Balmat and Dr. Michel-Gabriel Paccard.
Mont Blanc is the second-highest mountain in Europe after Mount Elbrus of Russia. It is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe. It rises 4,808 m (15,774 ft) above sea level and is ranked 11th in the world in topographic prominence. The mountain stands in a range called the Graian Alps, between the regions of Aosta Valley, Italy, and Savoie and Haute-Savoie, France. The location of the summit is on the watershed line between the valleys of Ferret and Veny in Italy and the valleys of Montjoie, and Arve in France, on the border between the two countries.
The Mont Blanc massif is popular for outdoor activities like hiking, climbing, trail running and winter sports like skiing, and snowboarding. The most popular route is the Goûter Route, which typically takes two days.
The three towns and their communes which surround Mont Blanc are Courmayeur in Aosta Valley, Italy; and Saint-Gervais-les-Bains and Chamonix in Haute-Savoie, France. The latter town was the site of the first Winter Olympics. A cable car ascends and crosses the mountain range from Courmayeur to Chamonix, through the Col du Géant. The 11.6 km (7 1⁄4-mile) Mont Blanc Tunnel, constructed between 1957 and 1965, runs beneath the mountain and is a major trans-Alpine transport route.
Michel Gabriel Paccard (1757–1827) was a Savoyard doctor and alpinist, citizen of the Kingdom of Sardinia.
Born in Chamonix, he studied medicine in Turin. Due to his passion for botany and minerals, he met Horace-Bénédict de Saussure, who initiated the race to be the first to ascend Mont Blanc.
Gaston Rébuffat wrote "Like Saussure a devotee of the natural sciences, he has a dream: to carry a barometer to the summit and take a reading there. An excellent mountaineer, he has already made several attempts."
Paccard had a first, unsuccessful, attempt in 1783 with Marc Theodore Bourrit. In 1784, he made several attempts with Jacques Balmat before they made the first ascent of Mont Blanc together on 8 August 1786.
Jacques Balmat, called Balmat du Mont Blanc (1762–1834) was a mountaineer, a Savoyard mountain guide, born in the Chamonix valley in Savoy, at this time part of the Kingdom of Sardinia.
A chamois hunter and collector of crystals, Balmat completed the first ascent of Mont Blanc with physician Michel-Gabriel Paccard on 8 August 1786. For this feat, King Victor Amadeus III gave him the honorary title du Mont Blanc.
Balmat and Paccard's ascent of Mont Blanc was a major accomplishment in the early history of mountaineering. C. Douglas Milner wrote "The ascent itself was magnificent; an amazing feat of endurance and sustained courage, carried through by these two men only, unroped and without ice axes, heavily burdened with scientific equipment and with long iron-pointed batons. The fortunate weather and a moon alone ensured their return alive."
Stamps issued by France and Monaco for the 200th anniversary of the first climbing
1898 Died: Eugène Boudin, French painter (b. 1824)
Eugène Louis Boudin (12 July 1824 – 8 August 1898) was one of the first French landscape painters to paint outdoors. Boudin was a marine painter, and expert in the rendering of all that goes upon the sea and along its shores. His pastels, summary and economic, garnered the splendid eulogy of Baudelaire; and Corot called him the "King of the skies".
Born at Honfleur, Boudin was the son of a harbor pilot, and at age 10 the young boy worked on a steamboat that ran between Le Havre and Honfleur. In 1835 the family moved to Le Havre, where Boudin's father opened a store for stationery and picture frames. Here the young Eugene worked, later opening his own small shop. Boudin's father had thus abandoned seafaring, and his son gave it up too, having no real vocation for it, though he preserved to his last days much of a sailor's character: frankness, accessibility, and open-heartedness.
In his shop, in which pictures were framed, Boudin came into contact with artists working in the area and exhibited in the shop the paintings of Constant Troyon and Jean-François Millet, who, along with Jean-Baptiste Isabey and Thomas Couture whom he met during this time, encouraged young Boudin to follow an artistic career. At the age of 22 he abandoned the world of commerce, started painting full-time, and travelled to Paris the following year and then through Flanders. In 1850 he earned a scholarship that enabled him to move to Paris, where he enrolled as a student in the studio of Eugène Isabey and worked as a copyist at the Louvre. To supplement his income he often returned to paint in Normandy and, from 1855, made regular trips to Brittany. On 14 January 1863 he married the 28-year-old Breton woman Marie-Anne Guédès in Le Havre and set up home in Paris.
Dutch 17th-century masters profoundly influenced him, and on meeting the Dutch painter Johan Jongkind, who had already made his mark in French artistic circles, Boudin was advised by his new friend to paint outdoors (en plein air). He also worked with Troyon and Isabey, and in 1859 met Gustave Courbet who introduced him to Charles Baudelaire, the first critic to draw Boudin's talents to public attention when the artist made his debut at the 1859 Paris Salon.
In 1857/58 Boudin befriended the young Claude Monet, then only 18, and persuaded him to give up his teenage caricature drawings and to become a landscape painter, helping to instill in him a love of bright hues and the play of light on water later evident in Monet's Impressionist paintings. The two remained lifelong friends and Monet later paid tribute to Boudin's early influence. Boudin joined Monet and his young friends in the first Impressionist exhibition in 1873, but never considered himself a radical or innovator.
Fair in Brittany, one of Boudin's "Brittany" paintings (1874), Corcoran Gallery of Art
Both Boudin and Monet lived abroad during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, Boudin in Antwerp and Monet in London; from 1873 to 1880 the Boudins lived in Bordeaux. His growing reputation enabled him to travel extensively at that time, visiting Belgium, the Netherlands and southern France. He continued to exhibit at the Paris Salons, receiving a third place medal at the Paris Salon of 1881, and a gold medal at the 1889 Exposition Universelle. In 1892 Boudin was made a knight of the Légion d'honneur, a somewhat tardy recognition of his talents and influence on the art of his contemporaries.
French stamp and First Day Cover depicting Boudin's works
1928 Died: Stjepan Radić, Croatian politician (b. 1871)
Stjepan Radić (11 June 1871 – 8 August 1928) was a Croatian politician and founder of the Croatian People's Peasant Party (HPSS).
He is credited with galvanizing Croatian peasantry into a viable political force. Throughout his entire career, Radić was opposed to the union and later Serb hegemony in Yugoslavia and became an important political figure in that country. He was shot in parliament by the Serbian radical politician Puniša Račić. Radić died several weeks later from a serious stomach wound at the age of 57. This assassination further alienated the Croats and the Serbs and initiated the breakdown of the parliamentary system, culminating in the 6 January Dictatorship of 1931.
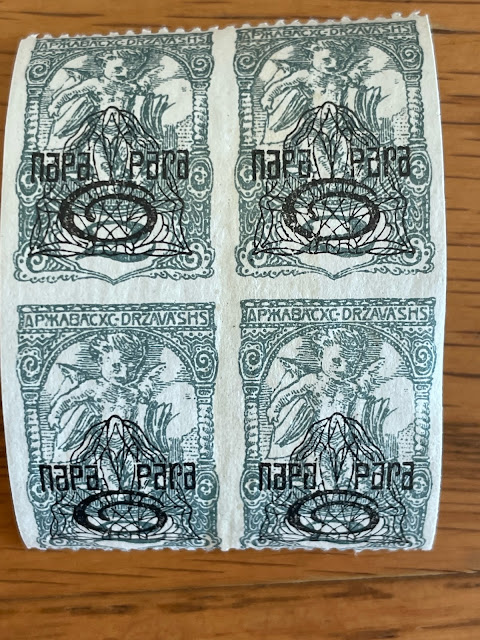
Croatian stamps issued to commemorate Radić
1929 – The German airship Graf Zeppelin begins a round-the-world flight.
LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin (Deutsches Luftschiff Zeppelin #127; Registration: D-LZ 127) was a German-built and -operated, passenger-carrying, hydrogen-filled, rigid airship which operated commercially from 1928 to 1937. It was named after the German pioneer of airships, Ferdinand von Zeppelin, who was a Graf or Count in the German nobility. During its operating life, the airship made 590 flights covering more than a million miles (1.6 million km). It was designed to be operated by a crew of 36 officers and men.