Here are some events that happened on December 1st. It could be an event or a person that died or was born on that day
1866 Born: George Everest, Welsh geographer and surveyor (b. 1790)
Colonel Sir George Everest (4 July 1790 – 1 December 1866) was a British surveyor and geographer who served as Surveyor General of India from 1830 to 1843. He is best known for having Mount Everest, the highest mountain on Earth, named in his honor.
After receiving a military education, Everest joined the East India Company and arrived in India at the age of 16. He was eventually made an assistant to William Lambton on the Great Trigonometric Survey, and replaced Lambton as superintendent of the survey in 1823. Everest was largely responsible for surveying the meridian arc from the southernmost point of India north to Nepal, a distance of about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 mi), a task which took from 1806 to 1841 to complete. He was made Surveyor General of India in 1830, retiring in 1843 and returning to England.
In 1865, the Royal Geographical Society renamed Peak XV – at the time only recently identified as the world's highest peak – in Everest's honor. Andrew Scott Waugh, his protégé and successor as surveyor general, had been responsible for putting his name forward in 1856. Everest's name was used as a compromise due to the difficulty of choosing between multiple local names for the mountain. He initially objected to the honor, as he had had nothing to do with its discovery and believed his name was not easily written or pronounced in Hindi
Cover and stamp issued by Great Britain to commemorate George Everest
1913 – Crete, having obtained self rule from Turkey after the First Balkan War, is annexed by Greece.
Crete (Greek: Κρήτη, Kríti; Ancient Greek: Κρήτη, Krḗtē) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. It bounds the southern border of the Aegean sea. Crete lies approximately 160 km (99 mi) south of the Greek mainland. It has an area of 8,336 km2 (3,219 sq mi) and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi).
Following the repeated uprisings in 1841, 1858, 1889, 1895 and 1897 by the Cretan people, who wanted to join Greece, the Great Powers decided to restore order and in February 1897 sent in troops. The island was subsequently garrisoned by troops from Great Britain, France, Italy and Russia; Germany and Austro-Hungary withdrawing from the occupation in early 1898. During this period Crete was governed through a committee of admirals from the remaining four Powers. In March 1898 the Powers decreed, with the very reluctant consent of the Sultan, that the island would be granted autonomy under Ottoman suzerainty in the near future.
In September 1898 an outbreak of rioting in Candia, modern Heraklion, left over 500 Cretan Christians, and 14 British servicemen, dead. As a result, the Admirals ordered the expulsion of all Ottoman troops and administrators from the island, a move that was ultimately completed by early November. The decision to grant autonomy to the island was enforced and a High Commissioner, Prince George of Greece, appointed, arriving to take up his post in December 1898. The flag of the Cretan State was chosen by the Powers, with the white star representing the Ottoman suzenraity over the island.
In 1905, disagreements between Prince George and minister Eleftherios Venizelos over the question of the enosis (union with Greece), such as the Prince's autocratic style of government, resulted in the Theriso revolt, one of leaders of which being Eleftherios Venizelos.
Prince George resigned as High Commissioner and was replaced by Alexandros Zaimis, a former Greek prime minister, in 1906. In 1908, taking advantage of domestic turmoil in Turkey as well as the timing of Zaimis's vacation away from the island, the Cretan deputies unilaterally declared union with Greece.
With the break out of the First Balkan War, the Greek government declared that Crete was since then part of the Greek territory. This was not recognized internationally until 1 December 1913
Greek stamp issued in 1913 to commemorate the union of Crete with Greece
1918 – The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later known as the Kingdom of Yugoslavia) is proclaimed.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia (Serbo-Croatian: Краљевина Југославија / Kraljevina Jugoslavija; Slovene: Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast Europe and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941, during the interwar period and beginning of World War II. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Serbo-Croatian: Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца / Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca; Slovene: Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev), but the term "Yugoslavia" (literally "Land of Southern Slavs") was its colloquial name due to its origins.The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929.
The preliminary kingdom was formed in 1918 by the merger of the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (itself formed from territories of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire) with the formerly independent Kingdom of Serbia. The Kingdom of Montenegro had united with Serbia five days previously, whereas the regions of Kosovo, Vojvodina, Vardar Macedonia and most of Bosnia were parts of Serbia prior to the unification.
The state was ruled by the Serb dynasty of Karađorđević, which previously ruled the Kingdom of Serbia under Peter I from 1903 (after the May Overthrow) onward. Peter I became the first king of Yugoslavia until his death in 1921. He was succeeded by his son Alexander I, who had been regent for his father. He was known as "Alexander the Unifier" and he renamed the kingdom "Yugoslavia" in 1929. He was assassinated in Marseille by Vlado Chernozemski, a member of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), during his visit to France in 1934. The crown passed to his then-still under-aged son Peter. Alexander's cousin Paul ruled as Prince regent until 1941, when Peter II came of age. The royal family flew to London the same year, prior to the country being invaded by the Axis powers.
In April 1941, the country was occupied and partitioned by the Axis powers. A royal government-in-exile, recognized by the United Kingdom and, later, by all the Allies, was established in London. In 1944, after pressure from the British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, the King recognized the government of Democratic Federal Yugoslavia as the legitimate government. This was established on 2 November following the signing of the Treaty of Vis by Ivan Šubašić (on behalf of the Kingdom) and Josip Broz Tito (on behalf of the Yugoslav Partisans).
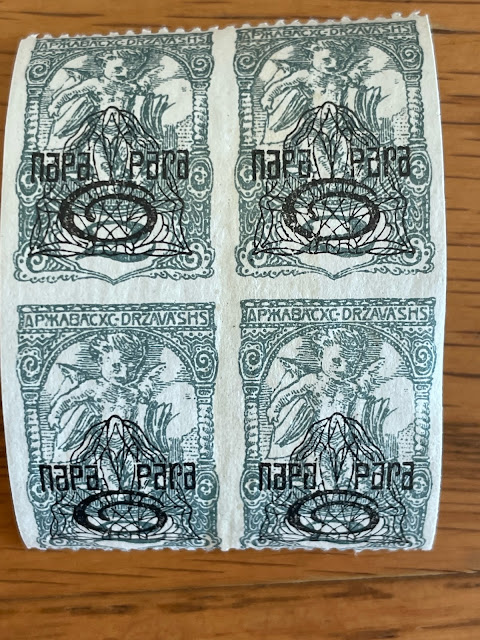
The first SHS stamps issued by Slovenia, Croatia and Bosnia
See also...
The revenge of Yugoslavia on Bosnian stamps of 1906
1973 Died: David Ben-Gurion, Israeli politician, 1st Prime Minister of Israel (b. 1886)
David Ben-Gurion (born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first Prime Minister of Israel. He was the preeminent leader of the Jewish community in British Mandate Palestine from 1935 until the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, which he led until 1963 with a short break in 1954-55.
Ben-Gurion's passion for Zionism, which began early in life, led him to become a major Zionist leader and Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization in 1946. As head of the Jewish Agency from 1935, and later president of the Jewish Agency Executive, he was the de facto leader of the Jewish community in Palestine, and largely led its struggle for an independent Jewish state in Mandatory Palestine. On 14 May 1948, he formally proclaimed the establishment of the State of Israel, and was the first to sign the Israeli Declaration of Independence, which he had helped to write. Ben-Gurion led Israel during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and united the various Jewish militias into the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Subsequently, he became known as "Israel's founding father".
Following the war, Ben-Gurion served as Israel's first Prime Minister and Minister of Defense. As Prime Minister, he helped build the state institutions, presiding over national projects aimed at the development of the country. He also oversaw the absorption of vast numbers of Jews from all over the world. A centerpiece of his foreign policy was improving relationships with the West Germans. He worked with Konrad Adenauer's government in Bonn, and West Germany provided large sums (in the Reparations Agreement between Israel and West Germany) in compensation for Nazi Germany's confiscation of Jewish property during the Holocaust.
In 1954 he resigned as Prime Minister and Minister of Defense but remained a member of the Knesset. He returned as Minister of Defense in 1955 after the Lavon Affair and the resignation of Pinhas Lavon. Later that year he became Prime Minister again, following the 1955 elections. Under his leadership, Israel responded aggressively to Arab guerrilla attacks, and in 1956, invaded Egypt along with British and French forces after Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal during what became known as the Suez Crisis.
He stepped down from office in 1963, and retired from political life in 1970. He then moved to Sde Boker, a kibbutz in the Negev desert, where he lived until his death. Posthumously, Ben-Gurion was named one of Time magazine's 100 Most Important People of the 20th century.
Israeli stamps depicting David Ben-Gurion