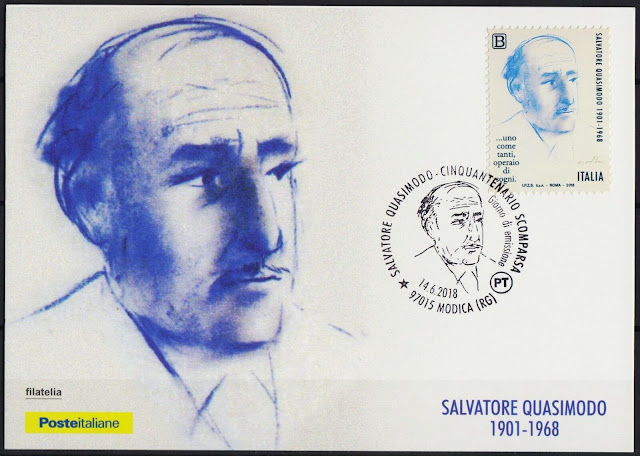
Sunday, June 14, 2020
June 14th in stamps Karl Landsteiner, Max Weber, Ernesto "Che" Guevara, Salvatore Quasimodo
Saturday, June 13, 2020
June 13th in stamps Egbert Bartholomeusz Kortenaer, Heinrich Hoffmann, Ludwig II, king of Bavaria
1665 Died: Egbert Bartholomeusz Kortenaer, Dutch admiral (b. 1604)
Egbert Bartholomeuszoon Kortenaer or Egbert Meussen Cortenaer (1604 – 13 June 1665) was an admiral of the United Provinces of the Netherlands who was killed in the Battle of Lowestoft.
Kortenaer was born in 1604 in Groningen of humble origins. In 1626, he was made boatswain, in 1636, second mate. In the First Anglo-Dutch War, he served as first mate in 1652 on the Dutch flagship, Brederode. In the Battle of Dungeness, he lost his right hand and eye. On 10 April 1653, he was made commandeur to replace flag captain Abel Roelants when Lieutenant-Admiral Maarten Tromp used Brederode as his flagship. In the Battle of Scheveningen, Tromp was killed. Kortenaer kept Tromp's standard raised to keep up morale (this was habitual for the Dutch on such occasions) and took command of his squadron. On 21 October 1653, Kortenaer was promoted to captain. In the years after the war, he often commanded squadrons as commodore when flag officers were absent.
In the Battle of the Sound (8 November 1658), serving as flag captain on Eendragt, he beat off every Swedish attack while his commanding officer, Lieutenant-Admiral Jacob van Wassenaer Obdam, was debilitated by gout. After this heroic conduct against the Swedish, Kortenaer was promoted to vice-admiral on 8 May 1659 and knighted by Frederick III of Denmark in the Order of the Elephant. On 29 January 1665, shortly before the Second Anglo-Dutch War, he was made lieutenant-admiral of the Admiralty of de Maze. He wasn't given command of the confederate Dutch fleet because he was a supporter of the House of Orange. A British intelligence report stated, "He is the best man they have".
During the Battle of Lowestoft on 13 June 1665, Kortenaer commanded the van and was second in overall command behind Van Wassenaer. He was fatally wounded early in the battle on Groot Hollandia by a cannonball hitting his hip and buried in Rotterdam in a marble grave memorial engraved with a poem by Gerard Brandt:
The Hero of the Maas, bereft of eye
and his right hand
Yet of the Wheel the Eye, Fist of
the Fatherland
KORTENAER the Great, the terror
of foe's fleets
the forcer of the Sound by this grave
his country greets
Stamps from Sint Maarten depicting Egbert Bartholomeuszoon Kortenaer
Heinrich Hoffmann (June 13, 1809 – September 20, 1894) was a German psychiatrist, who also wrote some short works including Der Struwwelpeter, an illustrated book portraying children misbehaving.
Hoffmann published poems and a satirical comedy before, in 1845, a publisher friend persuaded him to have a collection of illustrated children's verses printed which Hoffmann had done as Christmas present for his son. The book, later called Struwwelpeter after one of its anti-heroes, became popular with the public and had to be reprinted regularly; many foreign translations followed. "Struwwelpeter" was not perceived as cruel or overly moral by Hoffmann's contemporaries. The original title, "Funny stories and droll pictures", indicates that entertainment was at least partly the author's intention.
After the book's success, Hoffmann felt persuaded to write other children's books, of which only the first, König Nussknacker und der arme Reinhold, became popular.
He also kept on writing satires and (often comic) poems for adults. His satires show his strong skepticism towards all kinds of ideology and his distaste for religious, philosophical, or political bigotry. Even in Germany, he is today largely remembered for his Struwwelpeter.
Hoffmann was a man of liberal sympathies, campaigned for the goal of a constitutional monarchy, participated in the Vorparlament, and joined the Freemasons but later left due to their refusal to admit Jews.
German stamps depicting characters created by Heinrich Hoffmann
1886 Died: Ludwig II, king of Bavaria (b. 1845)
Ludwig II (German: Ludwig Otto Friedrich Wilhelm; English: Louis Otto Frederick William; 25 August 1845 – 13 June 1886) was King of Bavaria from 1864 until his death in 1886. He is sometimes called the Swan King or der Märchenkönig ("the Fairy Tale King"). He also held the titles of Count Palatine of the Rhine, Duke of Bavaria, Duke of Franconia, and Duke in Swabia.
Ludwig succeeded to the throne in 1864, aged 18. Two years later, Bavaria and Austria fought a war against Prussia lasting only a matter of weeks, which they lost. However, in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870, Bavaria sided with Prussia against France, and after the Prussian victory, it became part of the new German Empire led by Prussia. Though Bavaria retained a degree of autonomy on some matters within the new German Reich, Ludwig increasingly withdrew from day-to-day affairs of state in favour of extravagant artistic and architectural projects. He commissioned the construction of two lavish palaces and Neuschwanstein Castle, and he was a devoted patron of the composer Richard Wagner. Ludwig spent all his royal revenues (although not state funds as is commonly thought) on these projects, borrowed extensively, and defied all attempts by his ministers to restrain him. This extravagance was used against him to declare him insane, an accusation that has since come under scrutiny. Today, his architectural and artistic legacy includes many of Bavaria's most important tourist attractions.
German stamp depicting King Ludwig II of Bavaria
Friday, June 12, 2020
June 12th in stamps Helsinki, Roebling Brooklyn Bridge, Karl von Drais dandy horse, Frédéric Passy
1550 – The city of Helsinki, Finland (belonging to Sweden at the time) is founded by King Gustav I of Sweden.
Helsinki is the capital and most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of 650,058. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, making it by far the most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research. Helsinki is located 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 300 km (190 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close historical ties with these three cities.
Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen, and surrounding commuter towns, Helsinki forms the Greater Helsinki metropolitan area, which has a population of nearly 1.5 million. Often considered to be Finland's only metropolis, it is the world's northernmost metro area with over one million people as well as the northernmost capital of an EU member state. After Stockholm and Oslo, Helsinki is the third largest municipality in the Nordic countries. Finnish and Swedish are both official languages. The city is served by the international Helsinki Airport, located in the neighboring city of Vantaa, with frequent service to many destinations in Europe and Asia.
Helsinki was the World Design Capital for 2012, the venue for the 1952 Summer Olympics, and the host of the 52nd Eurovision Song Contest in 2007.
Helsinki has one of the world's highest urban standards of living. In 2011, the British magazine Monocle ranked Helsinki the world's most liveable city in its liveable cities index. In the Economist Intelligence Unit's 2016 liveability survey, Helsinki was ranked ninth among 140 cities.
Stamps issued in 1950 for the 400 year anniversary of the founding of Helsinki
1806 Born: John A. Roebling, German-American engineer, designed the Brooklyn Bridge (d. 1869)
John Augustus Roebling (born Johann August Röbling; June 12, 1806 – July 22, 1869) was a German-born American civil engineer. He designed and built wire rope suspension bridges, in particular the Brooklyn Bridge, which has been designated as a National Historic Landmark and a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.
The Brooklyn Bridge is a hybrid cable-stayed/suspension bridge in New York City, spanning the East River between the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn. Opened on May 24, 1883, the Brooklyn Bridge was the first fixed crossing across the East River. It was also the longest suspension bridge in the world at the time, with a main span of 1,595.5 feet (486.3 m) and a deck height of 127 ft (38.7 m) above mean high water. The span was originally called the New York and Brooklyn Bridge or the East River Bridge but was officially renamed the Brooklyn Bridge in 1915.
Proposals for a bridge connecting Manhattan and Brooklyn were first made in the early 19th century, which eventually led to the construction of the current span, designed by John A. Roebling. His son Washington Roebling oversaw the construction and contributed further design work, assisted by the latter's wife, Emily Warren Roebling. While construction started in 1870, numerous controversies and the novelty of the designed construction process caused the actual construction to be prolonged over thirteen years. Since opening, the Brooklyn Bridge has undergone several reconfigurations, having carried horse-drawn vehicles and elevated railway lines until 1950. To alleviate increasing traffic flows, additional bridges and tunnels were built across the East River. Following gradual deterioration, the Brooklyn Bridge has been renovated several times, including in the 1950s, 1980s, and 2010s.
The Brooklyn Bridge is the southernmost of four toll-free vehicular bridges connecting Manhattan Island and Long Island, with the Manhattan, Williamsburg, and Queensboro bridges to the north. Only passenger vehicles and pedestrian and bicycle traffic are permitted. A major tourist attraction since its opening, the Brooklyn Bridge has become an icon of New York City. Over the years, the bridge has been used as the location of various stunts and performances, as well as several crimes and attacks. The Brooklyn Bridge has been designated a National Historic Landmark, a New York City landmark, and a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.
Stamps and First Day Cover issued in 2006 by Germany to commemorate John Augustus Roebling
US First Day Cover issued for the 100th year anniversary of the opening of the Brooklyn Bridge
1817 – The earliest form of bicycle, the dandy horse, is driven by Karl von Drais.
Karl Freiherr von Drais (full name: Karl Friedrich Christian Ludwig Freiherr Drais von Sauerbronn) (29 April 1785 in Karlsruhe – 10 December 1851 in Karlsruhe) was a noble German forest official and significant inventor in the Biedermeier period.
Drais was a prolific inventor, who invented the Laufmaschine ("running machine"), also later called the velocipede, draisine (English) or draisienne (French), also nicknamed the hobby horse or dandy horse. This was his most popular and widely recognized invention. It incorporated the two-wheeler principle that is basic to the bicycle and motorcycle and was the beginning of mechanized personal transport. This was the earliest form of a bicycle, without pedals. His first reported ride from Mannheim to the "Schwetzinger Relaishaus" (a coaching inn, located in "Rheinau", today a district of Mannheim) took place on 12 June 1817 using Baden's best road. Karl rode his bike; it was a distance of about 7 kilometres (4.3 mi). The round trip took him a little more than an hour, but may be seen as the big bang for horseless transport. However, after marketing the velocipede, it became apparent that roads were so rutted by carriages that it was hard to balance on the machine for long, so velocipede riders took to the pavements and moved far too quickly, endangering pedestrians. Consequently, authorities in Germany, Great Britain, the United States, and even Calcutta banned its use, which ended its vogue for decades.
German stamp issued in 2017 for the 200th anniversary of the bicycle
Thursday, June 11, 2020
June 11th in stamps Richard Strauss, Stjepan Radić, Jacques Cousteau, John Wayne
He is credited with galvanizing Croatian peasantry into a viable political force. Throughout his entire career, Radić was opposed to the union and later Serb hegemony in Yugoslavia and became an important political figure in that country. He was shot in parliament by the Serbian radical politician Puniša Račić. Radić died several weeks later from a serious stomach wound at the age of 57. This assassination further alienated the Croats and the Serbs and initiated the breakdown of the parliamentary system, culminating in the 6 January Dictatorship of 1931.
Croatian stamps issued to commemorate Radić
1910 Born: Jacques Cousteau, French biologist, author, and inventor, co-developed the aqua-lung (d. 1997)
Jacques-Yves Cousteau (11 June 1910 – 25 June 1997) was a French naval officer, explorer, conservationist, filmmaker, innovator, scientist, photographer, author and researcher who studied the sea and all forms of life in water. He co-developed the Aqua-Lung, pioneered marine conservation and was a member of the Académie française.
Cousteau described his underwater world research in a series of books, perhaps the most successful being his first book, The Silent World: A Story of Undersea Discovery and Adventure, published in 1953. Cousteau also directed films, most notably the documentary adaptation of the book, The Silent World, which won a Palme d'or at the 1956 Cannes Film Festival. He remained the only person to win a Palme d'Or for a documentary film, until Michael Moore won the award in 2004 for Fahrenheit 9/11.
French stamp and First Day Cover issued to commemorate Jacques Cousteau
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
June 10th in stamps Jardin des Plantes, Nicolaus Otto, Antoni Gaudí
1793 – The Jardin des Plantes museum opens in Paris. A year later, it becomes the first public zoo.
The Jardin des plantes (French for "Garden of the Plants"), also known as the Jardin des plantes de Paris when distinguished from other jardins des plantes in other cities, is the main botanical garden in France. The term Jardin des plantes is the official name in the present day, but it is in fact an elliptical form of Jardin royal des plantes médicinales ("Royal Garden of the Medicinal Plants"), which is related to the original purpose of the garden back in the 17th century.
Headquarters of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle (National Museum of Natural History), the Jardin des plantes is situated in the 5th arrondissement, Paris, on the left bank of the river Seine, and covers 28 hectares (280,000 m²). Since 24 March 1993, the entire garden and its contained buildings, archives, libraries, greenhouses, ménagerie (a zoo), works of art, and specimens' collection are classified as a national historical landmark in France (labelled monument historique).
French stamps depicting Jardin des plantes
1832 Born: Nicolaus Otto, German engineer (d. 1891)
Nicolaus August Otto (14 June 1832, Holzhausen an der Haide, Nassau – 26 January 1891, Cologne) was a German engineer who successfully developed the compressed charge internal combustion engine which ran on petroleum gas and led to the modern internal combustion engine. The Association of German Engineers (VDI) created DIN standard 1940 which says "Otto Engine: internal combustion engine in which the ignition of the compressed fuel-air mixture is initiated by a timed spark", which has been applied to all engines of this type since.
German block of 4 depicting Nicolaus Otto
1926 Died: Antoni Gaudí, Spanish architect, designed the Park Güell (b. 1852)
Antoni Gaudí i Cornet (25 June 1852 – 10 June 1926) was a Catalan architect known as the greatest exponent of Catalan Modernism. Gaudí's works have a highly individualized, one-of-a-kind style. Most are located in Barcelona, including his main work, the church of the Sagrada Família.
Gaudí's work was influenced by his passions in life: architecture, nature, and religion. He considered every detail of his creations and integrated into his architecture such crafts as ceramics, stained glass, wrought ironwork forging and carpentry. He also introduced new techniques in the treatment of materials, such as trencadís which used waste ceramic pieces.
Under the influence of neo-Gothic art and Oriental techniques, Gaudí became part of the Modernista movement which was reaching its peak in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. His work transcended mainstream Modernisme, culminating in an organic style inspired by natural forms. Gaudí rarely drew detailed plans of his works, instead preferring to create them as three-dimensional scale models and moulding the details as he conceived them.
Gaudí's work enjoys global popularity and continuing admiration and study by architects. His masterpiece, the still-incomplete Sagrada Família, is the most-visited monument in Spain. Between 1984 and 2005, seven of his works were declared World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. Gaudí's Roman Catholic faith intensified during his life and religious images appear in many of his works. This earned him the nickname "God's Architect" and led to calls for his beatification.
Spanish stamps depicting Gaudi's works
Tuesday, June 09, 2020
June 9th in stamps Peter the Great, Bertha von Suttner, Carl Nielsen, Charles Dickens, Cole Porter
1672 Born: Peter the Great, Russian emperor (d. 1725)
Peter the Great (Peter I or Peter Alexeyevich 9 June 1672 – 8 February 1725) ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from 7 May 1682 until his death in 1725, jointly ruling before 1696 with his elder half-brother, Ivan V. Through a number of successful wars, he expanded the Tsardom into a much larger empire that became a major European power and also laid the groundwork for the Russian navy after capturing ports at Azov and the Baltic Sea. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment. Peter's reforms had a lasting impact on Russia, and many institutions of the Russian government trace their origins to his reign. He is also known for founding and developing the city of Saint Petersburg, which remained the capital of Russia until 1917.
Russian stamps depicting Peter the Great
1843 Born: Bertha von Suttner, Austrian journalist and author, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1914)
Bertha Felicitas Sophie Freifrau von Suttner (9 June 1843 – 21 June 1914) was an Austrian-Bohemian pacifist and novelist. In 1905, she became the second female Nobel laureate (after Marie Curie in 1903), the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, and the first Austrian laureate.
In 1889 Suttner became a leading figure in the peace movement with the publication of her pacifist novel, Die Waffen nieder! (Lay Down Your Arms!), which made her one of the leading figures of the Austrian peace movement. The book was published in 37 editions and translated into 12 languages. She witnessed the foundation of the Inter-Parliamentary Union and called for the establishment of the Austrian Gesellschaft der Friedensfreunde pacifist organisation in an 1891 Neue Freie Presse editorial. Suttner became chairwoman and also founded the German Peace Society the next year. She became known internationally as the editor of the international pacifist journal Die Waffen nieder!, named after her book, from 1892 to 1899. In 1897 she presented Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria with a list of signatures urging the establishment of an International Court of Justice and took part in the First Hague Convention in 1899 with the help of Theodor Herzl, who paid for her trip as a correspondent of the Zionist newspaper, Die Welt.
Upon her husband's death in 1902, Suttner had to sell Harmannsdorf Castle and moved back to Vienna. In 1904 she addressed the International Congress of Women in Berlin and for seven months travelled around the United States, attending a universal peace congress in Boston and meeting President Theodore Roosevelt.
Though her personal contact with Alfred Nobel had been brief, she corresponded with him until his death in 1896, and it is believed that she was a major influence on his decision to include a peace prize among those prizes provided in his will, which she was awarded in the fifth term on 10 December 1905. The presentation took place on 18 April 1906 in Kristiania.
German and Austrian stamps depicting Bertha von Suttner
1865 Born: Carl Nielsen, Danish violinist, composer, and conductor (d. 1931)
Carl August Nielsen (9 June 1865 – 3 October 1931) was a Danish composer, conductor and violinist, widely recognized as his country's most prominent composer.
Brought up by poor yet musically talented parents on the island of Funen, he demonstrated his musical abilities at an early age. He initially played in a military band before attending the Royal Danish Academy of Music in Copenhagen from 1884 until December 1886. He premiered his Op. 1, Suite for Strings, in 1888, at the age of 23. The following year, Nielsen began a 16-year stint as a second violinist in the Royal Danish Orchestra under the conductor Johan Svendsen, during which he played in Giuseppe Verdi's Falstaff and Otello at their Danish premieres. In 1916, he took a post teaching at the Royal Danish Academy and continued to work there until his death.
Although his symphonies, concertos and choral music are now internationally acclaimed, Nielsen's career and personal life were marked by many difficulties, often reflected in his music. The works he composed between 1897 and 1904 are sometimes ascribed to his "psychological" period, resulting mainly from a turbulent marriage with the sculptor Anne Marie Brodersen. Nielsen is especially noted for his six symphonies, his Wind Quintet and his concertos for violin, flute and clarinet. In Denmark, his opera Maskarade and many of his songs have become an integral part of the national heritage. His early music was inspired by composers such as Brahms and Grieg, but he soon developed his own style, first experimenting with progressive tonality and later diverging even more radically from the standards of composition still common at the time. Nielsen's sixth and final symphony, Sinfonia semplice, was written in 1924–25. He died from a heart attack six years later, and is buried in Vestre Cemetery, Copenhagen.
Nielsen maintained the reputation of a musical outsider during his lifetime, both in his own country and internationally. It was only later that his works firmly entered the international repertoire, accelerating in popularity from the 1960s through Leonard Bernstein and others. In Denmark, Nielsen's reputation was sealed in 2006 when three of his compositions were listed by the Ministry of Culture amongst the twelve greatest pieces of Danish music. For many years, he appeared on the Danish hundred-kroner banknote. The Carl Nielsen Museum in Odense documents his life and that of his wife. Between 1994 and 2009 the Royal Danish Library, sponsored by the Danish government, completed the Carl Nielsen Edition, freely available online, containing background information and sheet music for all of Nielsen's works, many of which had not been previously published.
Danish stamp depicting Carl Nielsen
1870 Died: Charles Dickens, English novelist and critic (b. 1812)
Charles John Huffam Dickens (7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime, and by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are still widely read today.
Born in Portsmouth, Dickens left school to work in a factory when his father was incarcerated in a debtors' prison. Despite his lack of formal education, he edited a weekly journal for 20 years, wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and non-fiction articles, lectured and performed readings extensively, was an indefatigable letter writer, and campaigned vigorously for children's rights, education, and other social reforms.
Dickens's literary success began with the 1836 serial publication of The Pickwick Papers. Within a few years he had become an international literary celebrity, famous for his humour, satire, and keen observation of character and society. His novels, most published in monthly or weekly instalments, pioneered the serial publication of narrative fiction, which became the dominant Victorian mode for novel publication. Cliffhanger endings in his serial publications kept readers in suspense. The installment format allowed Dickens to evaluate his audience's reaction, and he often modified his plot and character development based on such feedback. For example, when his wife's chiropodist expressed distress at the way Miss Mowcher in David Copperfield seemed to reflect her disabilities, Dickens improved the character with positive features. His plots were carefully constructed, and he often wove elements from topical events into his narratives. Masses of the illiterate poor chipped in ha'pennies to have each new monthly episode read to them, opening up and inspiring a new class of readers.
His 1843 novella A Christmas Carol remains especially popular and continues to inspire adaptations in every artistic genre. Oliver Twist and Great Expectations are also frequently adapted and, like many of his novels, evoke images of early Victorian London. His 1859 novel A Tale of Two Cities (set in London and Paris) is his best-known work of historical fiction. The most famous celebrity of his era, he undertook, in response to public demand, a series of public reading tours in the later part of his career. Dickens has been praised by many of his fellow writers—from Leo Tolstoy to George Orwell, G. K. Chesterton, and Tom Wolfe—for his realism, comedy, prose style, unique characterisations, and social criticism. However, Oscar Wilde, Henry James, and Virginia Woolf complained of a lack of psychological depth, loose writing, and a vein of sentimentalism.
The term Dickensian is used to describe something that is reminiscent of Dickens and his writings, such as poor social conditions or comically repulsive characters.
Stamps from Great Britain depicting Charles Dickens' works
1891 Born: Cole Porter, American composer and songwriter (d. 1964)
Cole Albert Porter (June 9, 1891 – October 15, 1964) was an American composer and songwriter. Many of his songs became standards noted for their witty, urbane lyrics, and many of his scores found success on Broadway and in film.
Born to a wealthy family in Indiana, Porter defied his grandfather's wishes and took up music as a profession. Classically trained, he was drawn to musical theatre. After a slow start, he began to achieve success in the 1920s, and by the 1930s he was one of the major songwriters for the Broadway musical stage. Unlike many successful Broadway composers, Porter wrote the lyrics as well as the music for his songs. After a serious horseback riding accident in 1937, Porter was left disabled and in constant pain, but he continued to work. His shows of the early 1940s did not contain the lasting hits of his best work of the 1920s and 1930s, but in 1948 he made a triumphant comeback with his most successful musical, Kiss Me, Kate. It won the first Tony Award for Best Musical.
Porter's other musicals include Fifty Million Frenchmen, DuBarry Was a Lady, Anything Goes, Can-Can and Silk Stockings. His numerous hit songs include "Night and Day", "Begin the Beguine", "I Get a Kick Out of You", "Well, Did You Evah!", "I've Got You Under My Skin", "My Heart Belongs to Daddy" and "You're the Top". He also composed scores for films from the 1930s to the 1950s, including Born to Dance (1936), which featured the song "You'd Be So Easy to Love"; Rosalie (1937), which featured "In the Still of the Night"; High Society (1956), which included "True Love"; and Les Girls (1957).
US stamp issued in 1991 depicting Cole Porter
Monday, June 08, 2020
June 8th in stamps Austro-Hungarian compromise, Andrew Jackson, Robert Schumann, Thomas Paine
1809 Died: Thomas Paine, English-American theorist and author (b. 1737)
Thomas Paine (born Thomas Pain) (February 9, 1737 [O.S. January 29, 1736] – June 8, 1809) was an English-born American political activist, philosopher, political theorist, and revolutionary. He authored the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution and inspired the patriots in 1776 to declare independence from Great Britain. His ideas reflected Enlightenment-era ideals of transnational human rights. Historian Saul K. Padover described him as "a corsetmaker by trade, a journalist by profession, and a propagandist by inclination".
Born in Thetford in the English county of Norfolk, Paine migrated to the British American colonies in 1774 with the help of Benjamin Franklin, arriving just in time to participate in the American Revolution. Virtually every rebel read (or listened to a reading of) his powerful pamphlet Common Sense (1776), proportionally the all-time best-selling American title, which catalysed the rebellious demand for independence from Great Britain. His The American Crisis (1776–1783) was a pro-revolutionary pamphlet series. Common Sense was so influential that John Adams said: "Without the pen of the author of Common Sense, the sword of Washington would have been raised in vain". Paine lived in France for most of the 1790s, becoming deeply involved in the French Revolution. He wrote Rights of Man (1791), in part a defense of the French Revolution against its critics. His attacks on Anglo-Irish conservative writer Edmund Burke led to a trial and conviction in absentia in England in 1792 for the crime of seditious libel.
The British government of William Pitt the Younger, worried by the possibility that the French Revolution might spread to England, had begun suppressing works that espoused radical philosophies. Paine's work, which advocated the right of the people to overthrow their government, was duly targeted, with a writ for his arrest issued in early 1792. Paine fled to France in September where, despite not being able to speak French, he was quickly elected to the French National Convention. The Girondists regarded him as an ally. Consequently, the Montagnards, especially Maximilien Robespierre, regarded him as an enemy.
In December 1793, he was arrested and was taken to Luxembourg Prison in Paris. While in prison, he continued to work on The Age of Reason (1793–1794). James Monroe, a future President of the United States, used his diplomatic connections to get Paine released in November 1794. Paine became notorious because of his pamphlets. The Age of Reason, in which he advocated deism, promoted reason and free thought and argued against institutionalized religion in general and Christian doctrine in particular. He published the pamphlet Agrarian Justice (1797), discussing the origins of property and introduced the concept of a guaranteed minimum income through a one-time inheritance tax on landowners. In 1802, he returned to the U.S. When he died on June 8, 1809 only six people attended his funeral as he had been ostracized for his ridicule of Christianity.
US Stamp and First Day Cover depicting Thomas Paine
1810 Born: Robert Schumann, German composer and critic (d. 1856)
Robert Schumann (8 June 1810 – 29 July 1856) was a German composer, pianist, and influential music critic. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Romantic era. Schumann left the study of law, intending to pursue a career as a virtuoso pianist. His teacher, Friedrich Wieck, a German pianist, had assured him that he could become the finest pianist in Europe, but a hand injury ended this dream. Schumann then focused his musical energies on composing.
In 1840, after a long and acrimonious legal battle with Wieck, who opposed the marriage, Schumann married Wieck's daughter Clara. A lifelong partnership in music began, as Clara herself was an established pianist and music prodigy. Clara and Robert also maintained a close relationship with German composer Johannes Brahms.
Until 1840, Schumann wrote exclusively for the piano. Later, he composed piano and orchestral works, and many Lieder (songs for voice and piano). He composed four symphonies, one opera, and other orchestral, choral, and chamber works. His best-known works include Carnaval, Symphonic Studies, Kinderszenen, Kreisleriana, and the Fantasie in C. Schumann was known for infusing his music with characters through motifs, as well as references to works of literature. These characters bled into his editorial writing in the Neue Zeitschrift für Musik (New Journal for Music), a Leipzig-based publication that he co-founded.
Schumann suffered from a mental disorder that first manifested in 1833 as a severe melancholic depressive episode—which recurred several times alternating with phases of "exaltation" and increasingly also delusional ideas of being poisoned or threatened with metallic items. What is now thought to have been a combination of bipolar disorder and perhaps mercury poisoning led to "manic" and "depressive" periods in Schumann's compositional productivity. After a suicide attempt in 1854, Schumann was admitted at his own request to a mental asylum in Endenich near Bonn. Diagnosed with psychotic melancholia, he died of pneumonia two years later at the age of 46, without recovering from his mental illness.
Stamps from Russia, East and West Germany depicting Robert Schumann
1845 Died: Andrew Jackson, American general, judge, and politician, 7th President of the United States (b. 1767)
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American soldier and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, Jackson gained fame as a general in the United States Army and served in both houses of the U.S. Congress. As president, Jackson sought to advance the rights of the "common man" against a "corrupt aristocracy" and to preserve the Union.
Born in the colonial Carolinas to a Scotch-Irish family in the decade before the American Revolutionary War, Jackson became a frontier lawyer and married Rachel Donelson Robards. He served briefly in the United States House of Representatives and the United States Senate, representing Tennessee. After resigning, he served as a justice on the Tennessee Supreme Court from 1798 until 1804. Jackson purchased a property later known as The Hermitage, and became a wealthy, slaveowning planter. In 1801, he was appointed colonel of the Tennessee militia and was elected its commander the following year. He led troops during the Creek War of 1813–1814, winning the Battle of Horseshoe Bend. The subsequent Treaty of Fort Jackson required the Creek surrender of vast lands in present-day Alabama and Georgia. In the concurrent war against the British, Jackson's victory in 1815 at the Battle of New Orleans made him a national hero. Jackson then led U.S. forces in the First Seminole War, which led to the annexation of Florida from Spain. Jackson briefly served as Florida's first territorial governor before returning to the Senate. He ran for president in 1824, winning a plurality of the popular and electoral vote. As no candidate won an electoral majority, the House of Representatives elected John Quincy Adams in a contingent election. In reaction to the alleged "corrupt bargain" between Adams and Henry Clay and the ambitious agenda of President Adams, Jackson's supporters founded the Democratic Party.
Jackson ran again in 1828, defeating Adams in a landslide. Jackson faced the threat of secession by South Carolina over what opponents called the "Tariff of Abominations." The crisis was defused when the tariff was amended, and Jackson threatened the use of military force if South Carolina attempted to secede. In Congress, Henry Clay led the effort to reauthorize the Second Bank of the United States. Jackson, regarding the Bank as a corrupt institution, vetoed the renewal of its charter. After a lengthy struggle, Jackson and his allies thoroughly dismantled the Bank. In 1835, Jackson became the only president to completely pay off the national debt, fulfilling a longtime goal. His presidency marked the beginning of the ascendancy of the party "spoils system" in American politics. In 1830, Jackson signed the Indian Removal Act, which forcibly relocated most members of the Native American tribes in the South to Indian Territory. The relocation process dispossessed the Indians and resulted in widespread death and disease. Jackson opposed the abolitionist movement, which grew stronger in his second term. In foreign affairs, Jackson's administration concluded a "most favored nation" treaty with Great Britain, settled claims of damages against France from the Napoleonic Wars, and recognized the Republic of Texas. In January 1835, he survived the first assassination attempt on a sitting president.
In his retirement, Jackson remained active in Democratic Party politics, supporting the presidencies of Martin Van Buren and James K. Polk. Though fearful of its effects on the slavery debate, Jackson advocated the annexation of Texas, which was accomplished shortly before his death. Jackson has been widely revered in the United States as an advocate for democracy and the common man. Many of his actions proved divisive, garnering both fervent support and strong opposition from many in the country. His reputation has suffered since the 1970s, largely due to his role in Native American removal. Surveys of historians and scholars have ranked Jackson favorably among U.S. presidents.
US Stamps depicting Andrew Jackson
1867 – Coronation of Franz Joseph as King of Hungary following the Austro-Hungarian compromise (Ausgleich).
The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 (German: Ausgleich, Hungarian: Kiegyezés) established the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary. The compromise put an end to the 18 years long military dictatorship and absolutist rule over Hungary, which was introduced by Francis Joseph after the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The Compromise partially re-established the former sovereignty of the Kingdom of Hungary, however being separate from, but no longer subject to the Austrian Empire. The agreement also restored the old historic constitution of the Kingdom of Hungary.
The Hungarian political leaders had two main goals during the negotiations. One was to regain the traditional status (both legal and political) of the Hungarian state, which was lost after the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The other was to restore the series of reform laws of the revolutionary parliament of 1848, which were based on the 12 points that established modern civil and political rights, economic and societal reforms in Hungary. Even the April Laws of the Hungarian revolutionary parliament (with the exception of the laws based on the 9th and 10th points) were restored by Francis Joseph.
Under the Compromise, the lands of the House of Habsburg were reorganized as a real union between the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary, headed by a single monarch who reigned as Emperor of Austria in the Austrian half of the empire, and as King of Hungary in Kingdom of Hungary. The Cisleithanian (Austrian) and Transleithanian (Hungarian) states were governed by separate parliaments and prime ministers. The two countries conducted unified foreign diplomatic and defense policies. For these purposes, "common" ministries of foreign affairs and defence were maintained under the monarch's direct authority, as was a third ministry responsible only for financing the two "common" portfolios.
The compromise remained bitterly unpopular among the ethnic Hungarian voters, because ethnic Hungarians did not vote for the ruling pro-compromise parties in the Hungarian parliamentary elections. Therefore the political maintenance of the Austro-Hungarian Compromise (thus Austria-Hungary itself) was mostly a result of the popularity of pro-compromise ruling Liberal Party among the ethnic minority voters in Kingdom of Hungary.
According to Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, "There were three of us who made the agreement: Deák, Andrássy and myself."
Hungarian stamps depicting Franz Joseph