1785 Born: Jacob Grimm, German philologist and mythologist (d. 1863)
Jacob Ludwig Karl Grimm (4 January 1785 – 20 September 1863), also known as Ludwig Karl, was a German philologist, jurist, and mythologist. He is known as the discoverer of Grimm's law of linguistics, the co-author of the monumental Deutsches Wörterbuch, the author of Deutsche Mythologie, and the editor of Grimm's Fairy Tales. He was the elder of the Brothers Grimm.
A collection of fairy tales was first published in 1812 by the Grimm brothers, known in English as Grimms' Fairy Tales.
From 1837–1841, the Grimm brothers joined five of their colleague professors at the University of Göttingen to form a group known as the Göttinger Sieben (The Göttingen Seven). They protested against Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover, whom they accused of violating the constitution. All seven were fired by the king.
Stamps from Germany, East Germany and Berlin featuring the Grimm brothers or their fairy tales
1809 Born: Louis Braille, French educator, invented Braille (d. 1852)
Stamps from France, Monaco, East Germany, Vatican, Serbia and Montenegro depicting Louis Braille
1878 – Russo-Turkish War (1877–78): Sofia is liberated from Ottoman rule and designated the capital of Liberated Bulgaria.
The Battle of Sofia (Bulgarian: Битката при София) was the culmination of Russian General Iosif Gurko's Western Squad for the defeat of the Orkhanie army in the Russo-Turkish War (1877-1878). It led to the Liberation of Sofia from Turkish rule.
The forces of the West group Gurko attacked in total offensive on 22 December / January 3. Column Lieutenant Velyaminov captured Kubratovo and Birimirtsi villages and went to Orlandovtsi village. The column of Major General Rauch captured the bridge at Chardakli farm (today, of the Tsarigradsko Shose over the Iskar river near Vrana Palace) and blocked the retreat route from Sofia towards Plovdiv. The Caucasian Cossack Brigade (commanded by Colonel Ivan Tutolmin) advanced in the direction Dărvenitsa - Boyana. Faced with a real threat of encirclement, Osman Nuri Pasha started a fast retreat in the direction of Pernik - Radomir, abandoning on the road 6000 wounded and sick soldiers. The foreign consuls (Vito Positano and Leander Lege) intervened, preventing an attempt to set fire to Sofia. On January 4, 1878 into Sofia entered the first Russian units: Caucasian Cossack brigade and Grodno Hussar Regiment. Large military ammunition depots and supplies were captured. In the cathedral, a service was celebrated in the presence of Lieutenant General Iosif Gurko and Major General Otto Rauch.
After the Battle of Sofia the Orkhanie Ottoman army ceased to exist as an organized military force. The Ottomans suffered irreparable human and material losses. This opened for offensive the direction of Sofia - Plovdiv - Edirne. Plovdiv was liberated on January 16 and Edirne was conquered on 20 January.
Bulgarian stamp commemorating 140 years of the Bulgarian army.
1880 Died: Anselm Feuerbach, German painter and educator (b. 1829)
Anselm Feuerbach (12 September 1829 – 4 January 1880) was a German painter. He was the leading classicist painter of the German 19th-century school.
His works are housed at leading public galleries in Germany. Stuttgart has the second version of Iphigenia; Karlsruhe, the Dante at Ravenna; Munich, the Medea; and Berlin, The Concert, his last important painting. Other major works include The Battle of the Amazons, Pietà, The Symposium of Plato, Orpheus and Eurydice and Ariosto in the Park of Ferrara
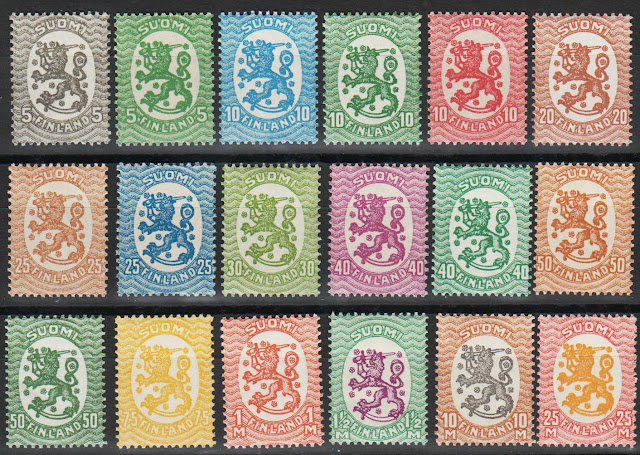
1918 – The Finnish Declaration of Independence is recognized by Russia, Sweden, Germany and France
The Finnish Declaration of Independence (Finnish: Suomen itsenäisyysjulistus; Swedish: Finlands självständighetsförklaring; Russian: Провозглашение независимости Финляндии) was adopted by the Parliament of Finland on 6 December 1917. It declared Finland an independent nation, among nations ending its autonomy within Russia as its Grand Duchy of Finland, with reference to a simultaneously delivered bill to the Diet to make Finland an independent republic instead.
On 2 November 1917, the Bolsheviks declared a general right of self-determination, including the right of complete secession, "for the Peoples of Russia". On the same day the Finnish Parliament issued a declaration by which it assumed, pro tempore, all powers of the Sovereign in Finland.
The old Instrument of Government was however no longer deemed suitable. Leading circles had long held monarchism and hereditary nobility to be antiquated, and advocated a republican constitution for Finland.
The Senate of Finland, the government that the Parliament had appointed in November, drafted a Declaration of Independence and a proposal for a new republican Instrument of Government. Chairman of the Senate (a.k.a. Prime minister) Pehr Evind Svinhufvud read the Declaration to the Parliament on 4 December. The Declaration of Independence was technically given the form of a preamble of the proposition, and was intended to be agreed by the Parliament, which adopted the Declaration on 6 December.
Declaring the independence was only part of the long process leading to the independence of Finland. The declaration is celebrated as the Independence Day in Finland.
1961 Died: Erwin Schrödinger, Austrian physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1887)
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as Erwin Schrodinger or Erwin Schroedinger, was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist who developed a number of fundamental results in the field of quantum theory: the Schrödinger equation provides a way to calculate the wave function of a system and how it changes dynamically in time.
In addition, he was the author of many works in various fields of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, colour theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book What Is Life? Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient and oriental philosophical concepts, ethics, and religion.He also wrote on philosophy and theoretical biology. He is also known for his "Schrödinger's cat" thought-experiment
Austrian stamp depicting Erwin Schrödinger
1965 Died: T. S. Eliot, English poet, playwright, critic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1888)
Thomas Stearns Eliot OM (26 September 1888 – 4 January 1965) was an American-born British poet, essayist, publisher, playwright, literary critic and editor. Born in St. Louis, Missouri, to a prominent Boston Brahmin family, he moved to England in 1914 at the age of 25 and went on to settle, work and marry there. He became a British subject in 1927 at the age of 39, subsequently renouncing his American citizenship.
Considered one of the 20th century's major poets, Eliot attracted widespread attention for his poem "The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock" in 1915, which was seen as a masterpiece of the Modernist movement. It was followed by some of the best-known poems in the English language, including "The Waste Land" (1922), "The Hollow Men" (1925), "Ash Wednesday" (1930), and Four Quartets (1943). He was also known for his seven plays, particularly Murder in the Cathedral (1935) and The Cocktail Party (1949). He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1948, "for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry".
Stamps from the US and Great Britain depicting T. S. Eliot and his work The Addressing of Cats