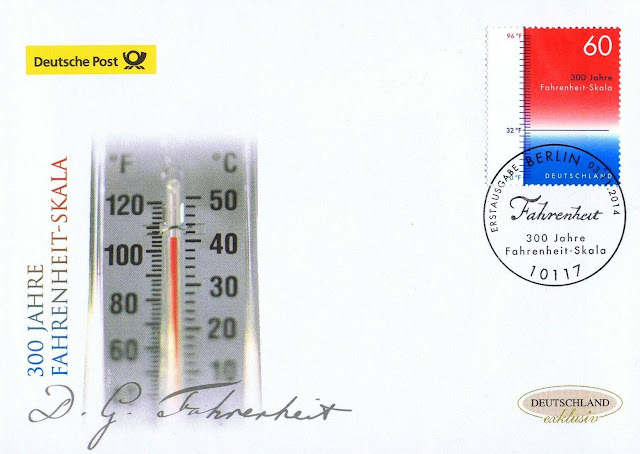
Sunday, August 16, 2020
September 16th in stamps Fahrenheit, Nicolas Baudin, Pedro V of Portugal
Saturday, August 15, 2020
August 15th in stamps Napoleon, Marquis de Lafayette, Ivan Meštrović
Lafayette was born into a wealthy land-owning family in Chavaniac in the province of Auvergne in south central France. He followed the family's martial tradition and was commissioned an officer at age 13. He became convinced that the American revolutionary cause was noble, and he traveled to the New World seeking glory in it. He was made a major general at age 19, but he was initially not given American troops to command. He was wounded during the Battle of Brandywine but still managed to organize an orderly retreat, and he served with distinction in the Battle of Rhode Island. In the middle of the war, he sailed for home to lobby for an increase in French support. He returned to America in 1780 and was given senior positions in the Continental Army. In 1781, troops under his command in Virginia blocked forces led by Cornwallis until other American and French forces could position themselves for the decisive Siege of Yorktown.
Lafayette returned to France and was appointed to the Assembly of Notables in 1787, convened in response to the fiscal crisis. He was elected a member of the Estates General of 1789, where representatives met from the three traditional orders of French society: the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners. After forming the National Constituent Assembly, he helped to write the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen with Thomas Jefferson's assistance. This document was inspired by the United States Declaration of Independence and invoked natural law to establish basic principles of the democratic nation-state. He also advocated the end of slavery, in keeping with the philosophy of natural liberty. After the storming of the Bastille, he was appointed commander-in-chief of France's National Guard and tried to steer a middle course through the years of revolution. In August 1792, radical factions ordered his arrest, and he fled into the Austrian Netherlands. He was captured by Austrian troops and spent more than five years in prison.
Lafayette returned to France after Napoleon Bonaparte secured his release in 1797, though he refused to participate in Napoleon's government. After the Bourbon Restoration of 1814, he became a liberal member of the Chamber of Deputies, a position which he held for most of the remainder of his life. In 1824, President James Monroe invited him to the United States as the nation's guest, and he visited all 24 states in the union and met a rapturous reception. During France's July Revolution of 1830, he declined an offer to become the French dictator. Instead, he supported Louis-Philippe as king, but turned against him when the monarch became autocratic. He died on 20 May 1834 and is buried in Picpus Cemetery in Paris, under soil from Bunker Hill. He is sometimes known as "The Hero of the Two Worlds" for his accomplishments in the service of both France and the United States.
US stamp and First Day Cover depicting Lafayette
Ivan Meštrović (15 August 1883 – 16 January 1962) was a renowned Yugoslavian and Croatian sculptor, architect and writer of the 20th century.
He was the most prominent sculptor of Croatian modern sculpture and a leading personality of artistic life in Zagreb. He studied at the Pavle Bilinić's Stone Workshop in Split and at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna, where he was formed under the influence of the Secession. He traveled throughout Europe and studied the works of ancient and Renaissance masters, especially Michelangelo, and French sculptors A. Rodin, A. Bourdelle and A. Maillola. He was the initiator of the national-romantic group Medulić (he advocated the creation of art of national features inspired by the heroic folk songs). During the First World War, he lived in emigration. After the war, he returned to Croatia and began a long and fruitful period of sculpture and pedagogical work. In 1942 he emigrated to Italy, in 1943 to Switzerland and in 1947 to the United States. He was a professor of sculpture at the Syracuse University and from 1955 at the University of Notre Dame in South Bend, Indiana.
Most of his early works of symbolic themes were formed in the spirit of the Secession, some of which, like the Well of Life, show impressionist restless surfaces created under the influence of Rodin's naturalism, and the second, reviving national myth, become stylized monumental plastics (Kosovo cycle, 1908-1910). Before the First World War, he left pathetic epic stylization, expressing increasingly emotional states, as evidenced by the wooden reliefs of biblical themes made in a combination of Archaic, Gothic, Secessionist and Expressionist styles. During the 1920s and 1930s, the classical component prevailed in his works. In this period, he created a number of public monuments of strong plastic expression, pronounced and legible shapes (Grgur Ninski and Marko Marulić in Split, Andrija Medulić, Andrija Kačić-Miošić and Josip Juraj Strossmayer in Zagreb, The Bowman and The Spearman in Chicago). Portraits take a special place in his opus.
Meštrović achieved works of strong plastic value in the construction-sculptural monuments and projects, mostly with central layout (the Mausoleum of the Račić family in Cavtat, the Mausoleum of the Meštrović family in Otavice, the Meštrović Pavilion in Zagreb, Monument to the Unknown Hero in Belgrade). He also designed a memorial church of King Zvonimir in Biskupija near Knin inspired by old Croatian churches, a representative family palace, today the Ivan Meštrović Gallery, and reconstructed renaissance fortified mansion Crikvine-Kaštilac in Split.
Friday, August 14, 2020
August 14th in stamps Hans Christian Ørsted, Cologne Cathedral, Paul Sabatier
Thursday, August 13, 2020
August 13th in stamps Delacroix, Hitchcock, H. G. Wells, August Bebel
1913 Died: August Bebel, German theorist and politician (b. 1840)
Ferdinand August Bebel (22 February 1840 – 13 August 1913) was a German socialist politician, writer, and orator. He is best remembered as one of the founders of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (SDAP) in 1869, which in 1875 merged with the General German Workers' Association into the Socialist Workers' Party of Germany (SAPD). During the repression under the terms of the Anti-Socialist Laws, Bebel became the leading figure of the social democratic movement in Germany and from 1892 until his death served as chairman of the Social Democratic Party of Germany.
Stamps from Germany and East Germany depicting Heinrich Hertz
Wednesday, August 12, 2020
August 12th in stamps Schrödinger, Thomas Mann, George Stephenson
In addition, he was the author of many works in various fields of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, colour theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book What Is Life? Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient and oriental philosophical concepts, ethics, and religion.He also wrote on philosophy and theoretical biology. He is also known for his "Schrödinger's cat" thought-experiment
Austrian stamp depicting Erwin Schrödinger
Tuesday, August 11, 2020
August 11th in stamps Babe Ruth, Pedro Nunes,Andrew Carnegie
George Herman "Babe" Ruth Jr. (February 6, 1895 – August 16, 1948) was an American professional baseball player whose career in Major League Baseball (MLB) spanned 22 seasons, from 1914 through 1935. Nicknamed "The Bambino" and "The Sultan of Swat", he began his MLB career as a star left-handed pitcher for the Boston Red Sox, but achieved his greatest fame as a slugging outfielder for the New York Yankees. Ruth established many MLB batting (and some pitching) records, including career home runs (714), runs batted in (RBIs) (2,213), bases on balls (2,062), slugging percentage (.690), and on-base plus slugging (OPS) (1.164); the last two still stand as of 2019. Ruth is regarded as one of the greatest sports heroes in American culture and is considered by many to be the greatest baseball player of all time. In 1936, Ruth was elected into the Baseball Hall of Fame as one of its "first five" inaugural members.
At age seven, Ruth was sent to St. Mary's Industrial School for Boys, a reformatory where he was mentored by Brother Matthias Boutlier of the Xaverian Brothers, the school's disciplinarian and a capable baseball player. In 1914, Ruth was signed to play minor-league baseball for the Baltimore Orioles but was soon sold to the Red Sox. By 1916, he had built a reputation as an outstanding pitcher who sometimes hit long home runs, a feat unusual for any player in the pre-1920 dead-ball era. Although Ruth twice won 23 games in a season as a pitcher and was a member of three World Series championship teams with the Red Sox, he wanted to play every day and was allowed to convert to an outfielder. With regular playing time, he broke the MLB single-season home run record in 1919.
After that season, Red Sox owner Harry Frazee sold Ruth to the Yankees amid controversy. The trade fueled Boston's subsequent 86-year championship drought and popularized the "Curse of the Bambino" superstition. In his 15 years with the Yankees, Ruth helped the team win seven American League (AL) pennants and four World Series championships. His big swing led to escalating home run totals that not only drew fans to the ballpark and boosted the sport's popularity but also helped usher in baseball's live-ball era, which evolved from a low-scoring game of strategy to a sport where the home run was a major factor. As part of the Yankees' vaunted "Murderers' Row" lineup of 1927, Ruth hit 60 home runs, which extended his MLB single-season record by a single home run. Ruth's last season with the Yankees was 1934; he retired from the game the following year, after a short stint with the Boston Braves. During his career, Ruth led the AL in home runs during a season 12 times.
During Ruth's career, he was the target of intense press and public attention for his baseball exploits and off-field penchants for drinking and womanizing. After his retirement as a player, he was denied the opportunity to manage a major league club, most likely due to poor behavior during parts of his playing career. In his final years, Ruth made many public appearances, especially in support of American efforts in World War II. In 1946, he became ill with nasopharyngeal cancer and died from the disease two years later. Ruth remains a part of American culture, and in 2018 President Donald Trump posthumously awarded him the Presidential Medal of Freedom.
Monday, August 10, 2020
August 10th in stamps Royal Greenwich Observatory, Louvre, Herbert Hoover, Maarten Tromp, Otto Lilienthal
1653 Died: Maarten Tromp, Dutch admiral (b. 1598)
Maarten Harpertszoon Tromp (also written as Maerten Tromp; 23 April 1598 – 10 August 1653) was a Dutch army general and admiral in the Dutch navy.
In 1637, Tromp was promoted from captain to Lieutenant-Admiral of Holland and West Frisia in 1637, following the dismissal of Lieutenant-Admiral Philips van Dorp, Vice-Admiral Jasper Liefhebber, and other flag officers due to incompetence. Although formally ranking under the Admiral-General Frederick Henry of Orange, he was the de facto supreme commander of the Dutch fleet, as the stadtholders never fought at sea. Tromp was mostly occupied with blockading the privateer port of Dunkirk. Both Tromp and Witte de With, who was named as Vice-Admiral, had been born in Den Briel and served as flag captains of Piet Heyn.
In 1639, during the Dutch struggle for independence from Spain, Tromp defeated a large Spanish fleet bound for Flanders at the Battle of the Downs, marking the end of Spanish naval power. In a preliminary battle, the Action of 18 September 1639, Tromp was the first fleet commander known for the deliberate use of line of battle tactics. His flagship in this period was the Aemilia.
In 1643 the subject was the center of a parliamentary investigation of naval intrigue with the Queen of England and the Prince of Orange who had allegedly instructed the Vice-Admiral to allow passage of two frigates purchased by English royalists in Dunkirk.
In the First Anglo-Dutch War of 1652 to 1653, Tromp commanded the Dutch fleet in the battles of Dover, Dungeness, Portland, the Gabbard and Scheveningen. In the latter, he was killed by a sharpshooter in the rigging of William Penn's ship. His acting flag captain, Egbert Bartholomeusz Kortenaer, on the Brederode kept up fleet morale by not lowering Tromp's standard, pretending Tromp was still alive.
Tromp's death was a severe blow to the Dutch navy but also to the Orangists, who sought the defeat of the Commonwealth of England and the restoration of the Stuart monarchy. Republican influence strengthened after Scheveningen, which led to peace negotiations with the Commonwealth, culminating in the Treaty of Westminster.
During his career, his main rival was Vice-Admiral Witte de With, who also served the Admiralty of Rotterdam (de Maze) from 1637. De With temporarily replaced him as supreme commander for the Battle of Kentish Knock. Tromp's successor was Lieutenant-Admiral Jacob van Wassenaer Obdam.
Dutch stamps depicting Maarten Tromp
1896 Died: Otto Lilienthal, German pilot and engineer (b. 1848 )
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders. Newspapers and magazines published photographs of Lilienthal gliding, favorably influencing public and scientific opinion about the possibility of flying machines becoming practical. On 9 August 1896, his glider stalled and he was unable to regain control. Falling from about 15 m (50 ft), he broke his neck and died the next day.
Lilienthal's greatest contribution was in the development of heavier-than-air flight. He made his flights from an artificial hill he built near Berlin and from natural hills, especially in the Rhinow region.
The filing of a U.S. Patent in 1894 by Lilienthal directed pilots to grip the "bar" for carrying and flying the hang glider. The A-frame of Percy Pilcher and Lilienthal echoes in today's control frame for hang gliders and ultralight aircraft. Working in conjunction with his brother Gustav, Lilienthal made over 2,000 flights in gliders of his design starting in 1891 with his first glider version, the Derwitzer, until his death in a gliding crash in 1896. His total flying time was five hours.
At the beginning, in 1891, Lilienthal succeeded with jumps and flights covering a distance of about 25 meters (82 ft). He could use the updraft of a 10 m/s wind against a hill to remain stationary with respect to the ground, shouting to a photographer on the ground to maneuver into the best position for a photo. In 1893, in the Rhinow Hills, he was able to achieve flight distances as long as 250 meters (820 ft). This record remained unbeaten for him or anyone else at the time of his death.
Lilienthal did research in accurately describing the flight of birds, especially storks, and used polar diagrams for describing the aerodynamics of their wings. He made many experiments in an attempt to gather reliable aeronautical data.
German stamps depicting Otto Lilienthal