1860 – Hugo Wolf, Slovene-Austrian composer (d. 1903)
Hugo Philipp Jacob Wolf (13 March 1860 – 22 February 1903) was an Austrian composer of Slovene origin, particularly noted for his art songs, or Lieder. He brought to this form a concentrated expressive intensity which was unique in late Romantic music, somewhat related to that of the Second Viennese School in concision but diverging greatly in technique.
Though he had several bursts of extraordinary productivity, particularly in 1888 and 1889, depression frequently interrupted his creative periods, and his last composition was written in 1898, before he suffered a mental collapse caused by syphilis.
Wolf wrote hundreds of lieder, three operas, incidental music, choral music, as well as some rarely heard orchestral, chamber and piano music. His most famous instrumental piece is the Italian Serenade (1887), originally for string quartet and later transcribed for orchestra, which marked the beginning of his mature style.
Wolf was famous for his use of tonality to reinforce meaning. Concentrating on two tonal areas to musically depict ambiguity and conflict in the text became a hallmark of his style, resolving only when appropriate to the meaning of the song. His chosen texts were often full of anguish and inability to find resolution, and thus so too was the tonality wandering, unable to return to the home key. Use of deceptive cadences, chromaticism, dissonance, and chromatic mediants obscure the harmonic destination for as long as the psychological tension is sustained. His formal structure as well reflected the texts being set, and he wrote almost none of the straightforward strophic songs favored by his contemporaries, instead building the form around the nature of the work.
1881 – Alexander II of Russia is assassinated.
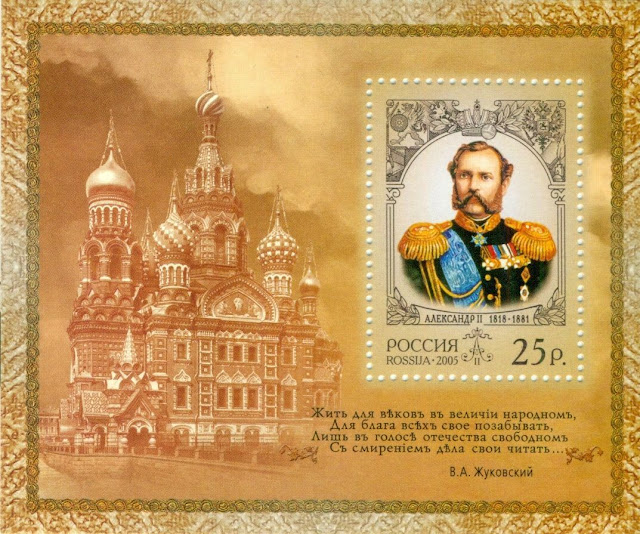
Alexander II (29 April 1818 – 13 March 1881) was the emperor of Russia from 2 March 1855 until his assassination on 13 March 1881. He was also the king of Poland and the grand duke of Finland.
Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was emancipation of Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator. The tsar was responsible for other reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the zemstvo system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promoting university education. After an assassination attempt in 1866, Alexander adopted a somewhat more reactionary stance until his death.
Alexander pivoted towards foreign policy and sold Alaska to the United States in 1867, fearing the remote colony would fall into British hands if there were another war. He sought peace, moved away from bellicose France when Napoleon III fell in 1871, and in 1872 joined with Germany and Austria in the League of the Three Emperors that stabilized the European situation. Despite his otherwise pacifist foreign policy, he fought a brief war with the Ottoman Empire in 1877–78, pursued further expansion into Siberia and the Caucasus, and conquered Turkestan. Although disappointed by the results of the Congress of Berlin in 1878, Alexander abided by that agreement. Among his greatest domestic challenges was an uprising in Poland in 1863, to which he responded by stripping that land of its separate constitution and incorporating it directly into Russia. Alexander was proposing additional parliamentary reforms to counter the rise of nascent revolutionary and anarchistic movements when he was assassinated in 1881.
Russian stamps depicting Alexander II
1906 Died Susan B. Anthony, American activist (b. 1820)
Susan B. Anthony (February 15, 1820 – March 13, 1906) was an American social reformer and women's rights activist who played a pivotal role in the women's suffrage movement. Born into a Quaker family committed to social equality, she collected anti-slavery petitions at the age of 17. In 1856, she became the New York state agent for the American Anti-Slavery Society.
In 1851, she met Elizabeth Cady Stanton, who became her lifelong friend and co-worker in social reform activities, primarily in the field of women's rights. In 1852, they founded the New York Women's State Temperance Society after Anthony was prevented from speaking at a temperance conference because she was female. In 1863, they founded the Women's Loyal National League, which conducted the largest petition drive in United States history up to that time, collecting nearly 400,000 signatures in support of the abolition of slavery. In 1866, they initiated the American Equal Rights Association, which campaigned for equal rights for both women and African Americans. In 1868, they began publishing a women's rights newspaper called The Revolution. In 1869, they founded the National Woman Suffrage Association as part of a split in the women's movement. In 1890, the split was formally healed when their organization merged with the rival American Woman Suffrage Association to form the National American Woman Suffrage Association, with Anthony as its key force. In 1876, Anthony and Stanton began working with Matilda Joslyn Gage on what eventually grew into the six-volume History of Woman Suffrage. The interests of Anthony and Stanton diverged somewhat in later years, but the two remained close friends.
In 1872, Anthony was arrested for voting in her hometown of Rochester, New York, and convicted in a widely publicized trial. Although she refused to pay the fine, the authorities declined to take further action. In 1878, Anthony and Stanton arranged for Congress to be presented with an amendment giving women the right to vote. Introduced by Sen. Aaron A. Sargent (R-CA), it later became known colloquially as the Susan B. Anthony Amendment. It was eventually ratified as the Nineteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1920.
Anthony traveled extensively in support of women's suffrage, giving as many as 75 to 100 speeches per year and working on many state campaigns. She worked internationally for women's rights, playing a key role in creating the International Council of Women, which is still active. She also helped to bring about the World's Congress of Representative Women at the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago in 1893.
When she first began campaigning for women's rights, Anthony was harshly ridiculed and accused of trying to destroy the institution of marriage. Public perception of her changed radically during her lifetime, however. Her 80th birthday was celebrated in the White House at the invitation of President William McKinley. She became the first female citizen to be depicted on U.S. coinage when her portrait appeared on the 1979 dollar coin.