Here are some events that happened on April 22nd. It could be an event or a person that died or was born on that day
1616 Died: Miguel de Cervantes, Spanish novelist, poet, and playwright (b. 1547)
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra (29 September 1547 (assumed) – 22 April 1616 ) was a Spanish writer widely regarded as the greatest writer in the Spanish language, and one of the world's pre-eminent novelists. He is best known for his novel Don Quixote, a work often cited as both the first modern novel, and one of the pinnacles of literature.
Much of his life was spent in poverty and obscurity, many of its details are disputed or unknown, and the bulk of his surviving work was produced in the three years preceding his death. Despite this, his influence and literary contribution are reflected by the fact Spanish is often referred to as "the language of Cervantes".
In 1569, Cervantes was forced to leave Spain and moved to Rome, where he worked in the household of a cardinal. In 1570, he enlisted in a Spanish Navy infantry regiment, and was badly wounded at the Battle of Lepanto in October 1571. He served as a soldier until 1575, when he was captured by Barbary pirates; after five years in captivity, he was ransomed, and returned to Madrid.
His first significant novel, titled La Galatea, was published in 1585, but he continued to work as a purchasing agent, then later a government tax collector. Part One of Don Quixote was published in 1605, Part Two in 1615. Other works include the 12 Novelas ejemplares (Exemplary Novels); a long poem, the Viaje del Parnaso (Journey to Parnassus); and Ocho comedias y ocho entremeses (Eight Plays and Eight Entr'actes). Los trabajos de Persiles y Sigismunda (The Travails of Persiles and Sigismunda), was published posthumously in 1616.
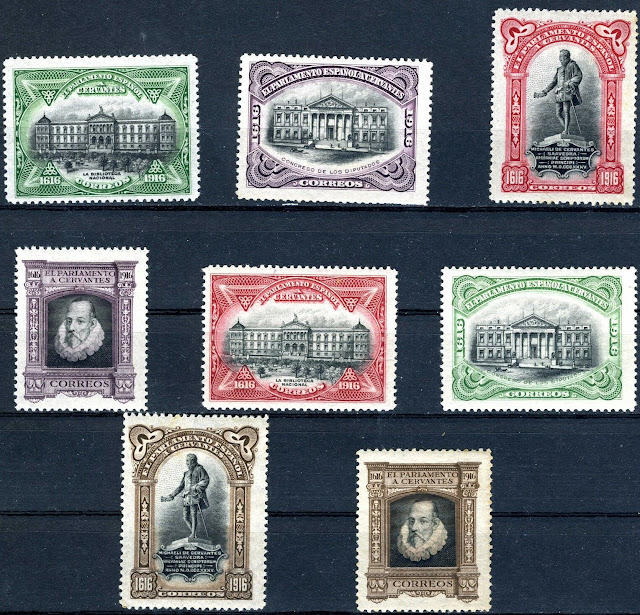
Stamps from various countries depicting Cervantes or his works
1854 Born: Henri La Fontaine, Belgian lawyer and author, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1943)
Henri La Fontaine (22 April 1854 – 14 May 1943), was a Belgian international lawyer and president of the International Peace Bureau. He received the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1913 because " he was the effective leader of the peace movement in Europe".
La Fontaine was born in Brussels on 22 April 1854 and studied law at the Free University of Brussels (now split into the Université libre de Bruxelles and the Vrije Universiteit Brussel). He was admitted to the bar in 1877 and established a reputation as an authority on international law. He and his sister Léonie La Fontaine were early advocates for women's rights and suffrage, founding in 1890 the Belgian League for the Rights of Women. In 1893, he became professor of international law at the Free University of Brussels and two years later was elected to the Belgian Senate as a member of the Socialist Party. He served as vice chairman of the Senate from 1919 to 1932.
La Fontaine took an early interest in the International Peace Bureau, founded in 1882, and was influential in the Bureau's efforts to bring about The Hague Peace Conferences of 1899 and 1907. He served as president of the Bureau from 1907 until his death in 1943. World War I convinced La Fontaine that the world would establish an international court when peace returned. He proposed a number of possible members, including Joseph Hodges Choate, Elihu Root, Charles William Eliot, and Andrew Dickson White. La Fontaine also promoted the idea of unification of the world's pacifist organizations.
He was a member of the Belgian delegation to the Paris Peace Conference in 1919 and to the League of Nations Assembly (1920–21). In other efforts to foster world peace, he founded the Centre Intellectuel Mondial (later merged into the League of Nations Institute for Intellectual Co-operation) and proposed such organizations as a world school and university, and a world parliament. In 1907, with Paul Otlet, he founded the Union of International Associations. He also is the co-founder of Institut International de Bibliographie (which later became the International Federation for Information and Documentation, FID) along with Paul Otlet. It was in this role that he and Otlet attended the World Congress of Universal Documentation in 1937.
Henri La Fontaine was a freemason, and a member of the lodge Les Amis Philanthropes in Brussels. He died on 14 May 1943 in Brussels.
Stamp from Belgium depicting Henri La Fontaine
1870 Born: Vladimir Lenin, Russian revolutionary and founder of Soviet Russia (d. 1924)
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov (22 April 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known by his alias Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1924 and of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1924. Under his administration, Russia, and later the Soviet Union, became a one-party Marxist–Leninist state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Ideologically a Marxist, he developed a variant of it known as Leninism.
Born to a moderately prosperous middle-class family in Simbirsk (now Ulyanovsk), Lenin embraced revolutionary socialist politics following his brother's 1887 execution. Expelled from Kazan Imperial University for participating in protests against the Russian Empire's Tsarist government, he devoted the following years to a law degree. He moved to Saint Petersburg in 1893 and became a senior Marxist activist. In 1897, he was arrested for sedition and exiled to Shushenskoye for three years, where he married Nadezhda Krupskaya. After his exile, he moved to Western Europe, where he became a prominent theorist in the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP). In 1903, he took a key role in the RSDLP ideological split, leading the Bolshevik faction against Julius Martov's Mensheviks. Following Russia's failed Revolution of 1905, he campaigned for the First World War to be transformed into a Europe-wide proletarian revolution, which as a Marxist he believed would cause the overthrow of capitalism and its replacement with socialism. After the 1917 February Revolution ousted the Tsar and established a Provisional Government, he returned to Russia to play a leading role in the October Revolution in which the Bolsheviks overthrew the new regime.
Lenin's Bolshevik government initially shared power with the Left Socialist Revolutionaries, elected soviets, and a multi-party Constituent Assembly, although by 1918 it had centralised power in the new Communist Party. Lenin's administration redistributed land among the peasantry and nationalised banks and large-scale industry. It withdrew from the First World War by signing a treaty conceding territory to the Central Powers, and promoted world revolution through the Communist International. Opponents were suppressed in the Red Terror, a violent campaign administered by the state security services; tens of thousands were killed or interned in concentration camps. His administration defeated right and left-wing anti-Bolshevik armies in the Russian Civil War from 1917 to 1922 and oversaw the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1921. Responding to wartime devastation, famine, and popular uprisings, in 1921 Lenin encouraged economic growth through the market-oriented New Economic Policy. Several non-Russian nations had secured independence from the Russian Empire after 1917, but three were re-united into the new Soviet Union in 1922. His health failing, Lenin died in Gorki, with Joseph Stalin succeeding him as the pre-eminent figure in the Soviet government.
Widely considered one of the most significant and influential figures of the 20th century, Lenin was the posthumous subject of a pervasive personality cult within the Soviet Union until its dissolution in 1991. He became an ideological figurehead behind Marxism–Leninism and thus a prominent influence over the international communist movement. A controversial and highly divisive historical figure, Lenin is viewed by supporters as a champion of socialism and the working class, while critics on both the left and right emphasize his role as founder and leader of an authoritarian regime responsible for political repression and mass killings.
Russian stamps depicting Lenin
1933 Died: Henry Royce, English engineer and businessman, co-founded Rolls-Royce Limited (b. 1863)
Sir Frederick Henry Royce, 1st Baronet(27 March 1863 – 22 April 1933) was an English engineer famous for his designs of car and aeroplane engines with a reputation for reliability and longevity. With Charles Rolls (1877 – 1910) and Claude Johnson (1864 – 1926), he founded Rolls-Royce.
Rolls-Royce initially focused on large 40-50 horsepower motor cars, the Silver Ghost and its successors. Royce produced his first aero engine shortly after the outbreak of the First World War and aircraft engines became Rolls-Royce's principal product.
Royce's health broke down in 1911 and he was persuaded to leave his factory in the Midlands at Derby and, taking a team of designers, move to the south of England spending winters in the south of France. He died at his home in Sussex in the spring of 1933.
Stamp and a booklet from Great Britain, Liechtenstein and Jersey depicting Rolls-Royce cars
1984 Died: Ansel Adams, American photographer and environmentalist (b. 1902)
Ansel Easton Adams (February 20, 1902 – April 22, 1984) was an American landscape photographer and environmentalist known for his black-and-white images of the American West. He helped found Group f/64, an association of photographers advocating "pure" photography which favored sharp focus and the use of the full tonal range of a photograph. He and Fred Archer developed an exacting system of image-making called the Zone System, a method of achieving a desired final print through a deeply technical understanding of how tonal range is recorded and developed in exposure, negative development, and printing. The resulting clarity and depth of such images characterized his photography.
Adams was a life-long advocate for environmental conservation, and his photographic practice was deeply entwined with this advocacy. At age 12, he was given his first camera during his first visit to Yosemite National Park. He developed his early photographic work as a member of the Sierra Club. He was later contracted with the United States Department of the Interior to make photographs of national parks. For his work and his persistent advocacy, which helped expand the National Park system, he was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1980.
Adams was a key advisor in establishing the photography department at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, an important landmark in securing photography's institutional legitimacy. He helped to stage that department's first photography exhibition, helped found the photography magazine Aperture, and co-founded the Center for Creative Photography at the University of Arizona.
US minisheet featuring Ansel Adam's works
1994 Died: Richard Nixon, American lieutenant, lawyer, and politician, 37th President of the United States (b. 1913)
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913 – April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, Nixon previously served as the 36th vice president from 1953 to 1961, having risen to national prominence as a representative and senator from California. After five years in the White House that saw the conclusion to the U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War, détente with the Soviet Union and China, and the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency, he became the only president to resign from the office, following the Watergate scandal.
Nixon was born into a poor family of Quakers in a small town in Southern California. He graduated from Duke University School of Law in 1937 and returned to California to practice law. He and his wife Pat moved to Washington in 1942 to work for the federal government. He served on active duty in the Navy Reserve during World War II. He was elected to the House of Representatives in 1946. His pursuit of the Hiss Case established his reputation as a leading anti-Communist which elevated him to national prominence. In 1950, he was elected to the Senate. He was the running mate of Dwight D. Eisenhower, the Republican Party's presidential nominee in the 1952 election, subsequently serving for eight years as the vice president. He unsuccessfully ran for president in 1960, narrowly losing to John F. Kennedy. Nixon then lost a race for governor of California to Pat Brown in 1962. In 1968, he ran for the presidency again and was elected, defeating Hubert Humphrey and George Wallace in a close election.
Nixon ended American involvement in Vietnam in 1973, ending the military draft that same year. Nixon's visit to China in 1972 eventually led to diplomatic relations between the two nations, and he gained the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty with the Soviet Union the same year. His administration generally transferred power from federal control to state control. He imposed wage and price controls for 90 days, enforced desegregation of Southern schools, established the Environmental Protection Agency, and began the War on Cancer. He also presided over the Apollo 11 Moon landing, which signaled the end of the Space Race. He was re-elected in one of the largest electoral landslides in American history in 1972 when he defeated George McGovern.
In his second term, Nixon ordered an airlift to resupply Israeli losses in the Yom Kippur War, a war which led to the oil crisis at home. By late 1973, Watergate escalated, costing Nixon much of his political support. On August 9, 1974, facing almost certain impeachment and removal from office, he became the first American president to resign. Afterwards, he was issued a pardon by his successor, Gerald Ford. In 20 years of retirement, Nixon wrote his memoirs and nine other books and undertook many foreign trips, rehabilitating his image into that of an elder statesman and leading expert on foreign affairs. He suffered a debilitating stroke on April 18, 1994, and died four days later at age 81. Surveys of historians and political scientists have ranked Nixon as a below-average president. However, evaluations of him have proven complex, with successes as president contrasted against the circumstances of his departure from office.
US stamp depicting Richard Nixon